


Next: Exploiting symmetries
Up: Choosing the Model
Previous: Number of hidden
The choice of activation function can change the
behaviour of the ANN network considerably.
Hidden units
The standard choice is the sigmoid function, eq. ( ), either in
symmetric
), either in
symmetric 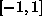 or asymmetric
or asymmetric 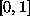 form. The sigmoid function is
global in the sense that it divides the feature space into two halves,
one where the response is approaching 1 and another where
it is approaching 0 (-1). Hence it is
very efficient for making sweeping cuts in the feature space.
form. The sigmoid function is
global in the sense that it divides the feature space into two halves,
one where the response is approaching 1 and another where
it is approaching 0 (-1). Hence it is
very efficient for making sweeping cuts in the feature space.
Other choices are the Gaussian bar [41], which replaces
the sigmoid function with a Gaussian, and the
radial basis function [42]. These are examples of local activation
functions that can be useful if the effective dimension of the problem
is lower than the actual number of variables, or if the problem is
local.
Output units
For classification tasks, the standard choice is the sigmoid. The outputs
can also be normalized, such that they sum to one, by using so-called
Potts or softmax output
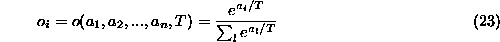
where 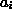 is the summed signal arriving at output i.
For function fitting problems the output should be chosen linear.
is the summed signal arriving at output i.
For function fitting problems the output should be chosen linear.
Of these, JETNET 3.0 implements all possibilities except for the
Gaussian bar and radial basis function.
It is sometimes suggested to use piecewise linear functions instead of
the more complicated hyperbolic tangent for the sigmoid, in order to
speed up the training procedure. We have not found any speedup whatsoever
when the simulations are run on RISC workstations. It might however be
relevant if the simulations are run on small personal computers.
System PRIVILEGED Account
Fri Feb 24 11:28:59 MET 1995
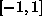 or asymmetric
or asymmetric 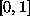 form. The sigmoid function is
global in the sense that it divides the feature space into two halves,
one where the response is approaching 1 and another where
it is approaching 0 (-1). Hence it is
very efficient for making sweeping cuts in the feature space.
form. The sigmoid function is
global in the sense that it divides the feature space into two halves,
one where the response is approaching 1 and another where
it is approaching 0 (-1). Hence it is
very efficient for making sweeping cuts in the feature space.
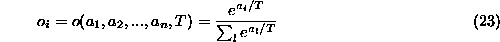
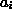 is the summed signal arriving at output i.
For function fitting problems the output should be chosen linear.
is the summed signal arriving at output i.
For function fitting problems the output should be chosen linear.